How to prevent emails from going to spam in Microsoft Hotmail or Outlook?

Matthew Whittaker
Co-founder & CTO, Suped
Published 5 Aug 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
5 min read

 Getting your emails into the inbox of Microsoft Hotmail and
Getting your emails into the inbox of Microsoft Hotmail and  Outlook.com recipients can be a significant challenge for email marketers and businesses. Their filtering systems are among the most stringent, often diverting even legitimate messages into the junk or spam folder. This can severely impact your engagement rates and the effectiveness of your email campaigns.
Outlook.com recipients can be a significant challenge for email marketers and businesses. Their filtering systems are among the most stringent, often diverting even legitimate messages into the junk or spam folder. This can severely impact your engagement rates and the effectiveness of your email campaigns. Microsoft (formerly Hotmail) evaluates incoming mail.
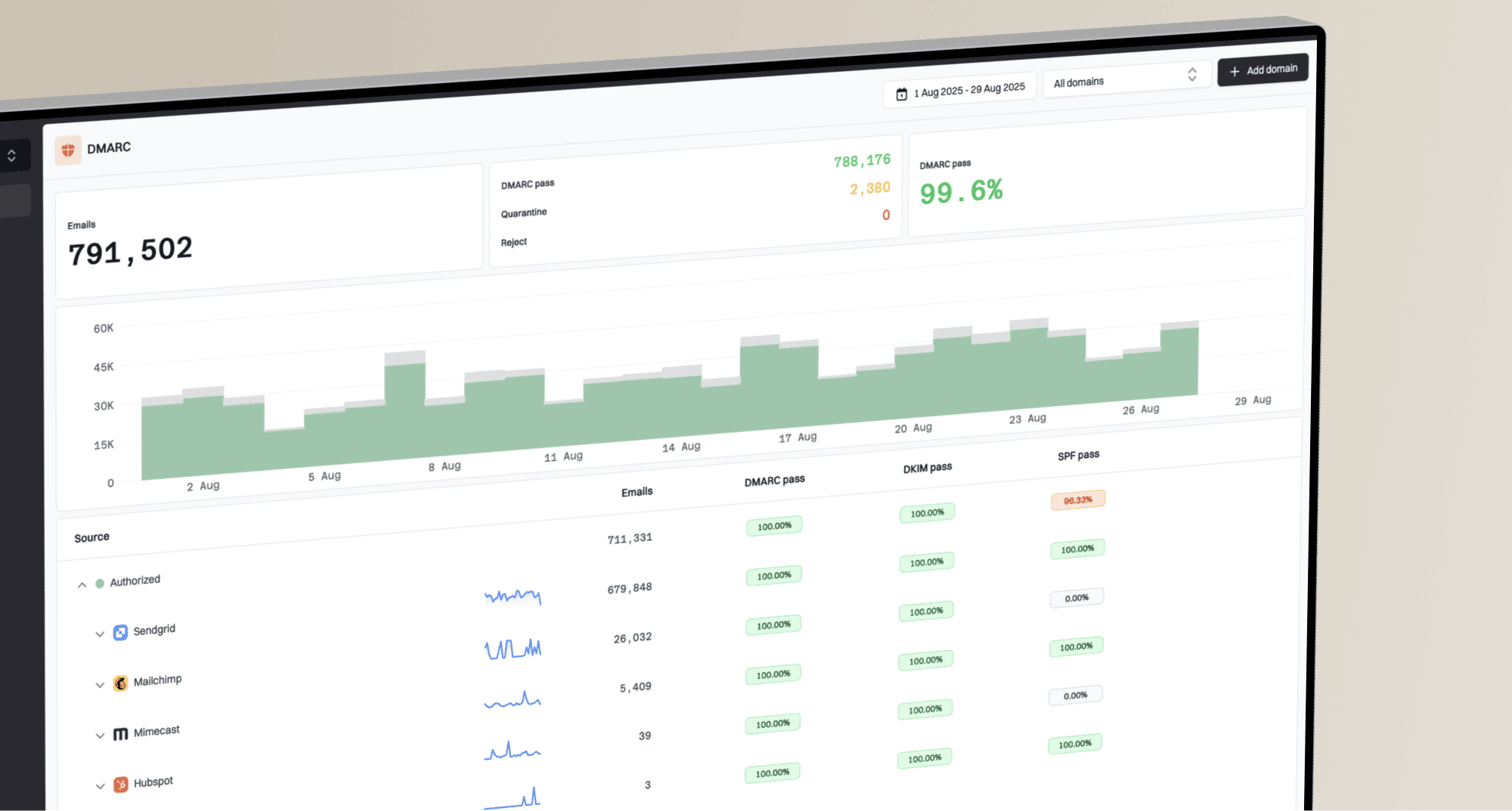
Microsoft (formerly Hotmail) evaluates incoming mail. Microsoft's filters analyze the overall content for suspicious patterns, disproportionate image-to-text ratios, and hidden text.
Microsoft's filters analyze the overall content for suspicious patterns, disproportionate image-to-text ratios, and hidden text. Microsoft's complex filtering, proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC setup verifies your identity as a legitimate sender. This tells email providers that your emails haven't been forged or tampered with.
Microsoft's complex filtering, proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC setup verifies your identity as a legitimate sender. This tells email providers that your emails haven't been forged or tampered with. Microsoft's new sender requirements in 2024, DMARC is becoming increasingly mandatory for bulk senders. If your emails are still hitting the junk folder, double-check your DMARC records and ensure they are aligned with your sending practices.
Microsoft's new sender requirements in 2024, DMARC is becoming increasingly mandatory for bulk senders. If your emails are still hitting the junk folder, double-check your DMARC records and ensure they are aligned with your sending practices. Microsoft's filters are highly sensitive to user behavior and perceived content quality.
Microsoft's filters are highly sensitive to user behavior and perceived content quality. Microsoft's filters.
Microsoft's filters. Microsoft systems, helping to avoid the junk folder.
Microsoft systems, helping to avoid the junk folder. Microsoft's filters, which can be particularly opaque.
Microsoft's filters, which can be particularly opaque. Microsoft might embed. Sometimes, a blocklist (or blacklist) listing could be the culprit, even if it's not immediately apparent.
Microsoft might embed. Sometimes, a blocklist (or blacklist) listing could be the culprit, even if it's not immediately apparent. Microsoft's filters, so foster positive interactions and clean your lists regularly.
Microsoft's filters, so foster positive interactions and clean your lists regularly.