Why are my emails landing in Office 365 spam folders?

Michael Ko
Co-founder & CEO, Suped
Published 26 Jul 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
7 min read

 Office 365, can be a frustrating experience. It disrupts communication, impacts business operations, and can severely damage your sender reputation. While you might assume your emails are perfectly fine, Microsoft's robust spam filters are constantly evaluating incoming mail. This guide will explore the primary reasons why your legitimate emails might be diverted to the junk folder in Office 365 and what actionable steps you can take to prevent it.
Office 365, can be a frustrating experience. It disrupts communication, impacts business operations, and can severely damage your sender reputation. While you might assume your emails are perfectly fine, Microsoft's robust spam filters are constantly evaluating incoming mail. This guide will explore the primary reasons why your legitimate emails might be diverted to the junk folder in Office 365 and what actionable steps you can take to prevent it. Gmail and Office 365. For more information, read our guide on what SPF means in email.
Gmail and Office 365. For more information, read our guide on what SPF means in email.v=spf1 include:spf.protection.outlook.com -all
 Outlook (via spf.protection.outlook.com) to send emails on your domain's behalf and sets a hard fail (-all) for all other sources. Ensure all your legitimate sending services are included.
Outlook (via spf.protection.outlook.com) to send emails on your domain's behalf and sets a hard fail (-all) for all other sources. Ensure all your legitimate sending services are included. Microsoft'sSmart Network Data Services (SNDS) and
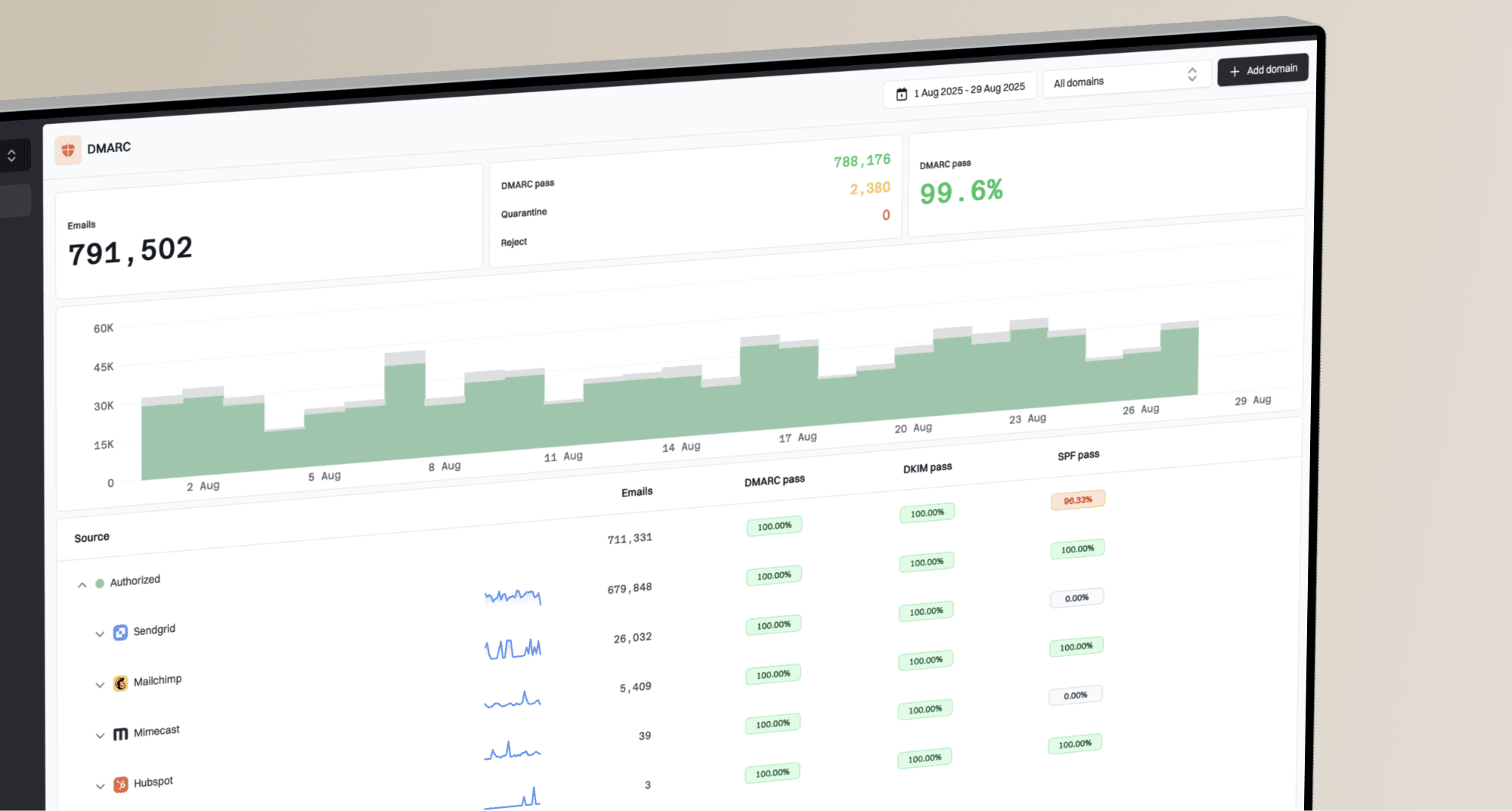
Microsoft'sSmart Network Data Services (SNDS) and  GooglePostmaster Tools. These provide valuable insights into your domain's health and any potential issues that Office 365 or Gmail might be seeing.
GooglePostmaster Tools. These provide valuable insights into your domain's health and any potential issues that Office 365 or Gmail might be seeing.