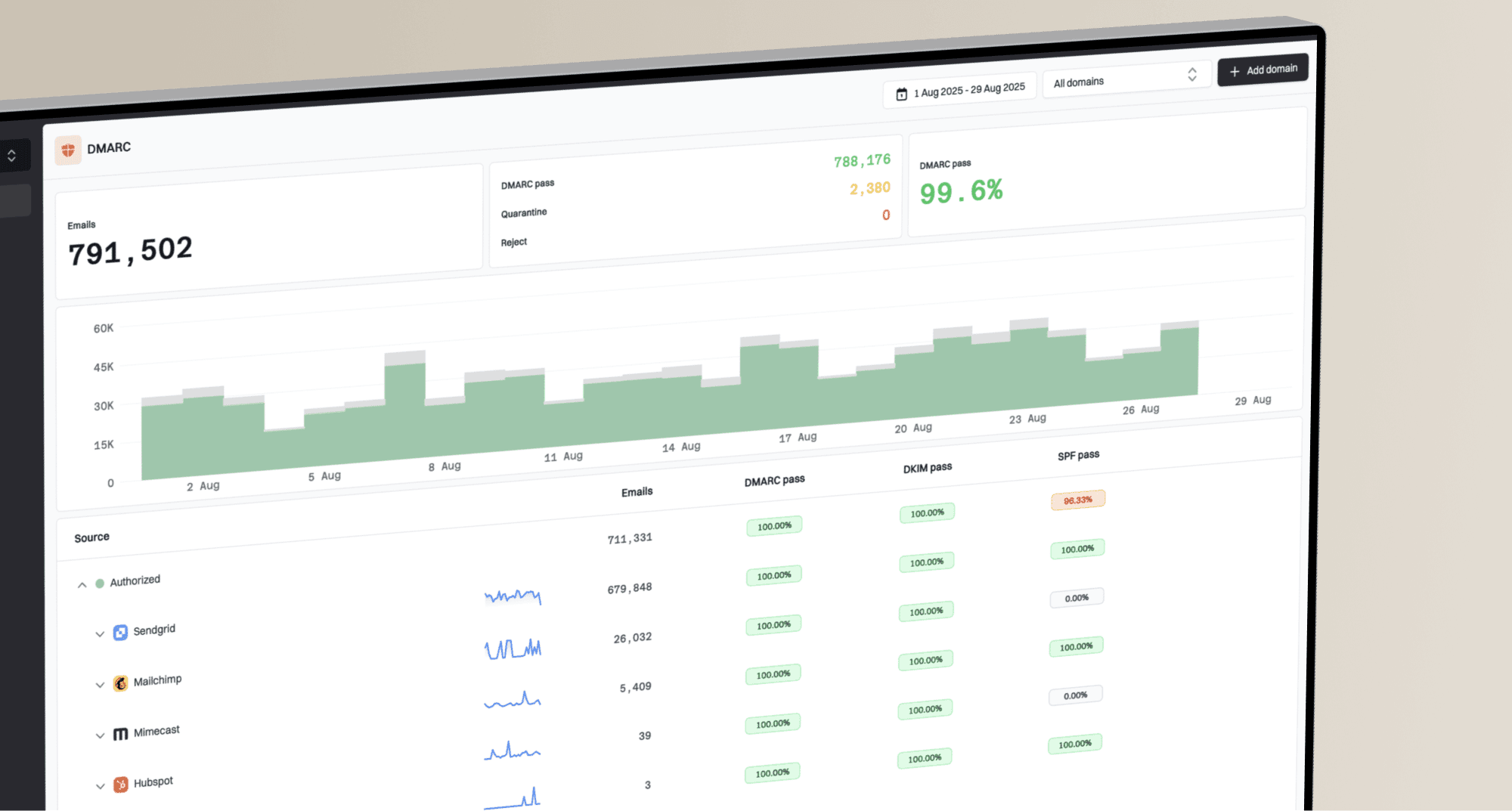
How to correctly filter Gmail addresses and understand Google's sending requirements for B2B email?

Michael Ko
Co-founder & CEO, Suped
Published 20 May 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
7 min read

 Google Workspace for their email services.
Google Workspace for their email services. Google's hosting, are generally treated differently by mail filters than generic '@gmail.com' addresses.
Google's hosting, are generally treated differently by mail filters than generic '@gmail.com' addresses. Google Workspace for email, regardless of whether it's an '@gmail.com' address.
Google Workspace for email, regardless of whether it's an '@gmail.com' address. Gmail's bulk sender policies.
Gmail's bulk sender policies. Gmail's bulk sender policies.
Gmail's bulk sender policies. Google Workspace, maximizing your deliverability to key contacts.
Google Workspace, maximizing your deliverability to key contacts. Gmail accounts; they set a new industry standard that other providers are rapidly adopting. Ignoring these requirements means risking significant deliverability issues, even for B2B communications.
Gmail accounts; they set a new industry standard that other providers are rapidly adopting. Ignoring these requirements means risking significant deliverability issues, even for B2B communications. Google Workspace (e.g., jane.smith@yourcompany.com). While both might show MX records pointing to Google, the latter is a business account. Google's new rules differentiate between these, with stricter enforcement for bulk senders targeting personal email addresses.
Google Workspace (e.g., jane.smith@yourcompany.com). While both might show MX records pointing to Google, the latter is a business account. Google's new rules differentiate between these, with stricter enforcement for bulk senders targeting personal email addresses. Google Workspace should generally have good deliverability if you adhere to the sender requirements. However, if you are sending cold outreach or bulk marketing to personal Gmail accounts, you must be extremely diligent about compliance. Avoiding sending limits is critical.
Google Workspace should generally have good deliverability if you adhere to the sender requirements. However, if you are sending cold outreach or bulk marketing to personal Gmail accounts, you must be extremely diligent about compliance. Avoiding sending limits is critical.v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com ~all
 Gmail's filters. Consider how spam filters operate to improve deliverability.
Gmail's filters. Consider how spam filters operate to improve deliverability. Google Workspace, and completely excluding them from your outreach will limit your business opportunities.
Google Workspace, and completely excluding them from your outreach will limit your business opportunities. Gmail, but are becoming universal best practices across the email industry. By adhering to these, you ensure your B2B emails reach a wider, more engaged audience and avoid being unnecessarily blocked or blacklisted (or blocklisted).
Gmail, but are becoming universal best practices across the email industry. By adhering to these, you ensure your B2B emails reach a wider, more engaged audience and avoid being unnecessarily blocked or blacklisted (or blocklisted). Google. Adhering to the updated sender requirements – especially robust authentication, low spam rates, and easy unsubscribes – is paramount for successful deliverability in the current email landscape.
Google. Adhering to the updated sender requirements – especially robust authentication, low spam rates, and easy unsubscribes – is paramount for successful deliverability in the current email landscape. Google Workspace-hosted business account.
Google Workspace-hosted business account.