Why are my transactional emails from Sendgrid being flagged as spam in Gmail, and how can I fix it?

Matthew Whittaker
Co-founder & CTO, Suped
Published 10 Jul 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
8 min read

 SendGrid, inexplicably end up in the spam folder for
SendGrid, inexplicably end up in the spam folder for  Gmail recipients. You've checked your basic setup, and everything seems fine, yet crucial communications like password resets, order confirmations, or renewal notices are being misdirected. This isn't just an annoyance; it directly impacts user experience and trust.
Gmail recipients. You've checked your basic setup, and everything seems fine, yet crucial communications like password resets, order confirmations, or renewal notices are being misdirected. This isn't just an annoyance; it directly impacts user experience and trust. Gmail attempts to protect its users from unwanted or malicious content. Sometimes, legitimate emails can get caught in this net.
Gmail attempts to protect its users from unwanted or malicious content. Sometimes, legitimate emails can get caught in this net. SendGrid's robust infrastructure, if
SendGrid's robust infrastructure, if  Gmail (or any mailbox provider) starts flagging your emails, it usually points to specific factors related to your sending behavior, domain, or content. While authentication is crucial, it's often not the sole reason once initial setup is complete.
Gmail (or any mailbox provider) starts flagging your emails, it usually points to specific factors related to your sending behavior, domain, or content. While authentication is crucial, it's often not the sole reason once initial setup is complete. SendGrid to be flagged as spam by
SendGrid to be flagged as spam by  Gmail. It's essential to pinpoint which of these might be affecting your particular sending patterns.
Gmail. It's essential to pinpoint which of these might be affecting your particular sending patterns. Google's algorithms. For example, a renewal email that heavily promotes new product features rather than simply informing the user about their upcoming renewal might be misclassified.
Google's algorithms. For example, a renewal email that heavily promotes new product features rather than simply informing the user about their upcoming renewal might be misclassified. Gmail might flag them as suspicious or phishing attempts. This is particularly true if
Gmail might flag them as suspicious or phishing attempts. This is particularly true if  SendGrid is using a generic click-tracking domain (like `sendgrid.net`) instead of a custom, branded one. This can negatively impact your sender reputation, making your emails more susceptible to being blacklisted or blocklisted. You can read more about avoiding spam blocking in this SendGrid guide.
SendGrid is using a generic click-tracking domain (like `sendgrid.net`) instead of a custom, branded one. This can negatively impact your sender reputation, making your emails more susceptible to being blacklisted or blocklisted. You can read more about avoiding spam blocking in this SendGrid guide. Gmail's advanced filters. Here's a breakdown of common problems:
Gmail's advanced filters. Here's a breakdown of common problems: SendGrid links resolve to `sendgrid.net` instead of your branded domain, it can hurt your reputation. Configure
SendGrid links resolve to `sendgrid.net` instead of your branded domain, it can hurt your reputation. Configure  SendGrid's link branding to use your own domain.
SendGrid's link branding to use your own domain. SendGrid to send on your behalf and doesn't exceed the 10-lookup limit.
SendGrid to send on your behalf and doesn't exceed the 10-lookup limit. SendGrid is signing your emails. Learn about common DKIM selectors.
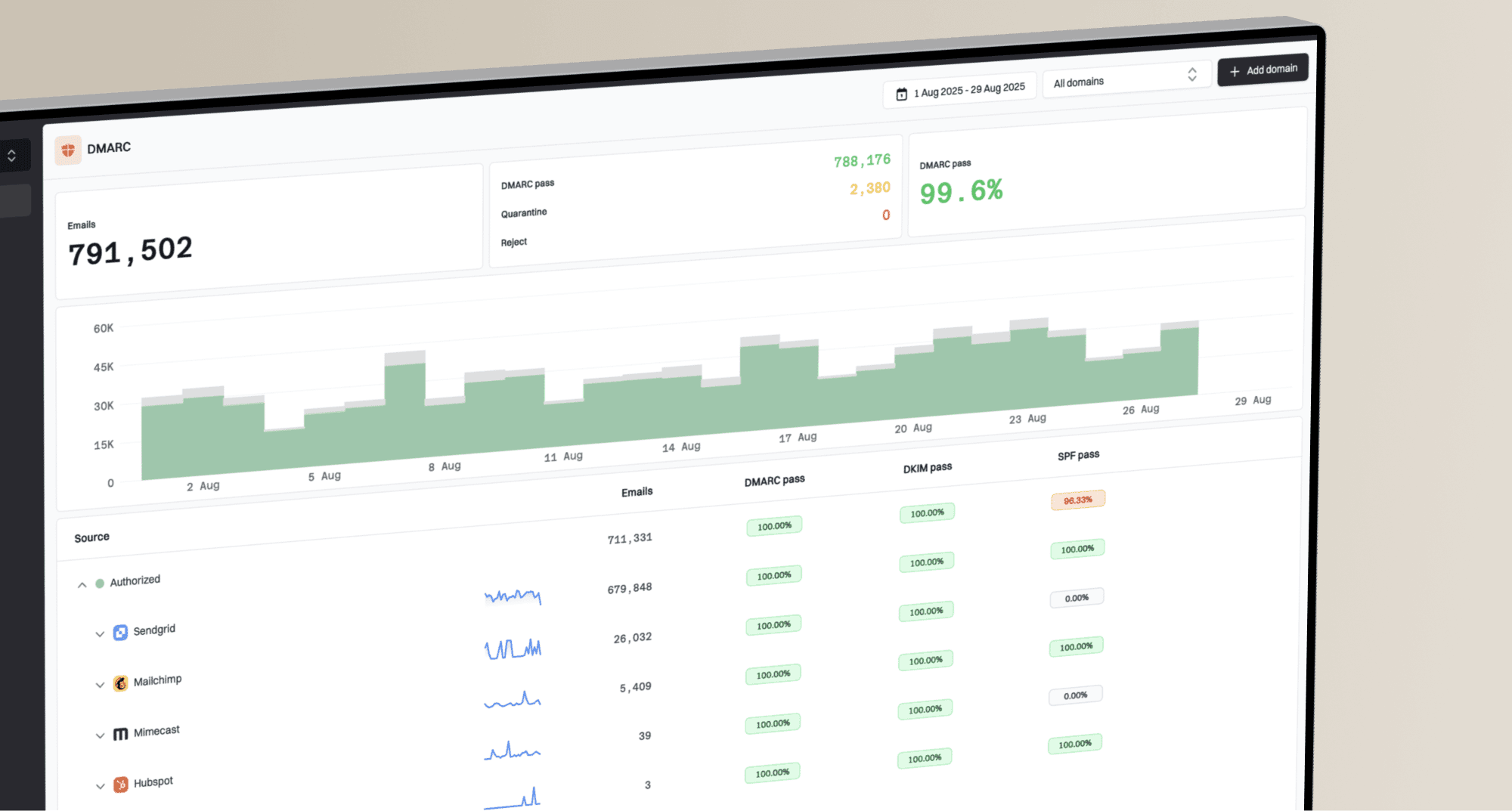
SendGrid is signing your emails. Learn about common DKIM selectors. Google provides invaluable insights into your domain's reputation, spam complaints, and authentication status. If your domain reputation is low, that's a strong indicator of a widespread problem. Monitoring DMARC reports will also highlight any authentication failures.
Google provides invaluable insights into your domain's reputation, spam complaints, and authentication status. If your domain reputation is low, that's a strong indicator of a widespread problem. Monitoring DMARC reports will also highlight any authentication failures. Gmail's filters. If you’ve recently added new links or redesigned your landing pages, carefully inspect them for anything that could be perceived as phishing. Even small details, like a login form on a page with minimal surrounding context, can trigger warnings. Additionally, ensure your
Gmail's filters. If you’ve recently added new links or redesigned your landing pages, carefully inspect them for anything that could be perceived as phishing. Even small details, like a login form on a page with minimal surrounding context, can trigger warnings. Additionally, ensure your  SendGrid account has link branding enabled, so click-tracked links use your own domain, not a generic `sendgrid.net` subdomain. This simple step can significantly improve trust signals.
SendGrid account has link branding enabled, so click-tracked links use your own domain, not a generic `sendgrid.net` subdomain. This simple step can significantly improve trust signals. SendGrid manages its shared IP reputation, a sudden drop in deliverability could indicate an issue there, or if you have a dedicated IP, it might be listed. Regularly checking major blocklists is a proactive measure.
SendGrid manages its shared IP reputation, a sudden drop in deliverability could indicate an issue there, or if you have a dedicated IP, it might be listed. Regularly checking major blocklists is a proactive measure. SendGrid, requires consistent attention to your email program's health.
SendGrid, requires consistent attention to your email program's health. Gmail (and other mailbox providers) often treat different subdomains or sending IPs as distinct entities for reputation purposes.
Gmail (and other mailbox providers) often treat different subdomains or sending IPs as distinct entities for reputation purposes. SendGrid flagged as spam by
SendGrid flagged as spam by  Gmail is a common yet solvable challenge. It typically boils down to a combination of factors related to your domain's reputation, email content, link quality, and proper authentication. It’s crucial to treat each of these areas with diligence, understanding that
Gmail is a common yet solvable challenge. It typically boils down to a combination of factors related to your domain's reputation, email content, link quality, and proper authentication. It’s crucial to treat each of these areas with diligence, understanding that  Gmail's filters are designed to protect users from both unwanted bulk mail and malicious phishing attempts.
Gmail's filters are designed to protect users from both unwanted bulk mail and malicious phishing attempts.