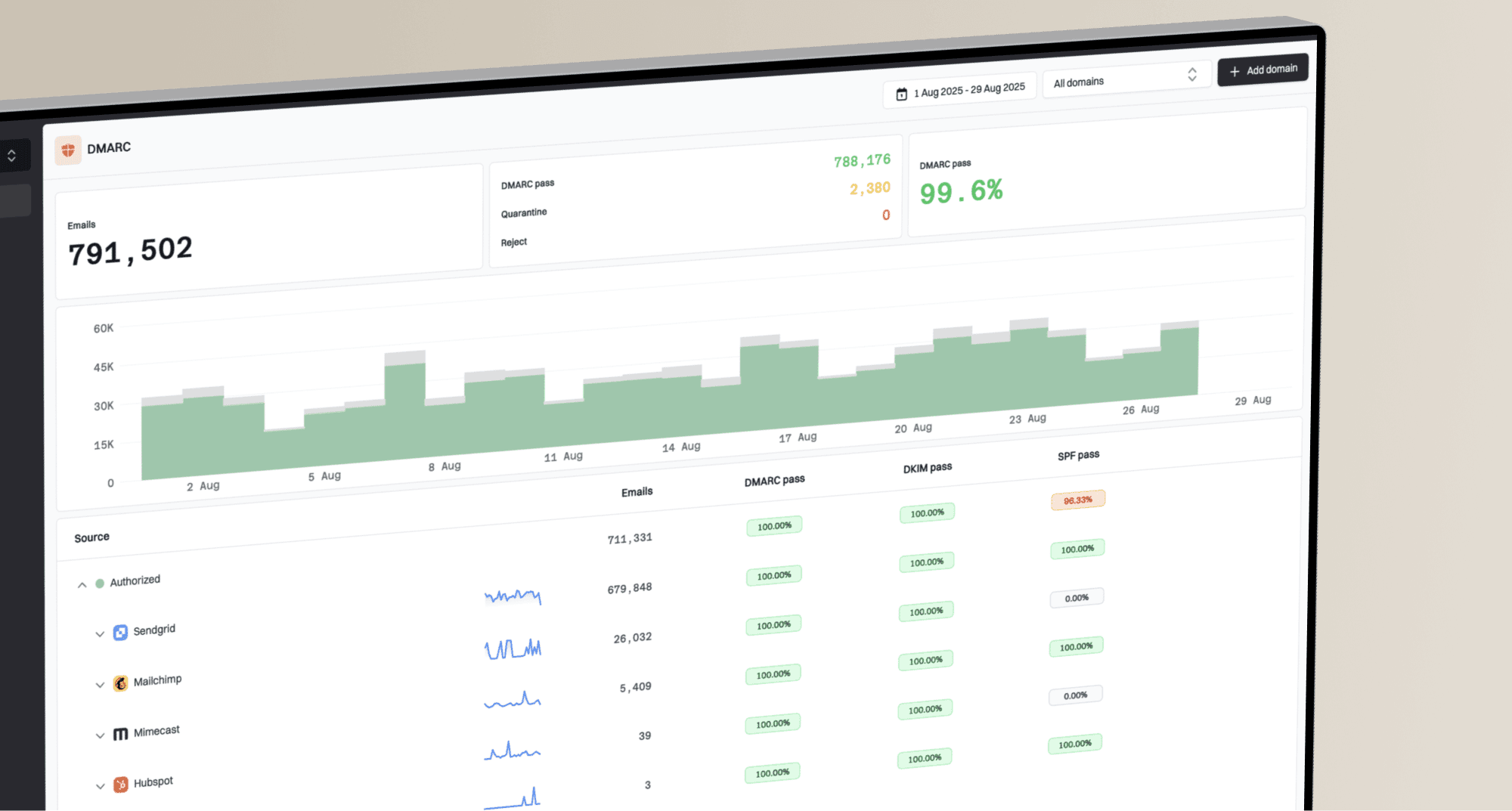
Why does Gmail say it cannot verify the sender and mark the email as spam?

Matthew Whittaker
Co-founder & CTO, Suped
Published 28 Jun 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
8 min read

 Gmail stating it cannot verify the sender or that an email might be spam can be unsettling, especially when you know the email is legitimate. This warning often appears as a grayed-out icon next to the sender's name, accompanied by a note like The Webby Mail cannot verify that this sender is not a spammer. It's a clear signal that something is amiss with your email's authentication or overall deliverability health.
Gmail stating it cannot verify the sender or that an email might be spam can be unsettling, especially when you know the email is legitimate. This warning often appears as a grayed-out icon next to the sender's name, accompanied by a note like The Webby Mail cannot verify that this sender is not a spammer. It's a clear signal that something is amiss with your email's authentication or overall deliverability health. Google's sophisticated spam filters flag an email, it's often due to unverified sender information, leading to messages being routed to the spam folder or displaying prominent warnings. Understanding the root causes is the first step toward a fix.
Google's sophisticated spam filters flag an email, it's often due to unverified sender information, leading to messages being routed to the spam folder or displaying prominent warnings. Understanding the root causes is the first step toward a fix. Gmail and other mailbox providers rely on a set of protocols to confirm that an email truly originates from the domain it claims to be from. Without these checks, it's easy for malicious actors to impersonate legitimate senders, leading to phishing and spam. When these checks fail,
Gmail and other mailbox providers rely on a set of protocols to confirm that an email truly originates from the domain it claims to be from. Without these checks, it's easy for malicious actors to impersonate legitimate senders, leading to phishing and spam. When these checks fail,  Gmail displays the 'cannot verify sender' warning and increases the likelihood of the email being marked as spam.
Gmail displays the 'cannot verify sender' warning and increases the likelihood of the email being marked as spam. Gmail displaying an unverified sender warning or marking your emails as spam (also called a blocklist or blacklist entry). The most common culprits revolve around misconfigured or missing DNS records for authentication. An improperly set up SPF record, such as one with syntax errors or that doesn't include all authorized sending IPs, is a frequent cause. For instance, a common mistake is having multiple SPF records or including unexpected characters, which can break the record and prevent proper verification.
Gmail displaying an unverified sender warning or marking your emails as spam (also called a blocklist or blacklist entry). The most common culprits revolve around misconfigured or missing DNS records for authentication. An improperly set up SPF record, such as one with syntax errors or that doesn't include all authorized sending IPs, is a frequent cause. For instance, a common mistake is having multiple SPF records or including unexpected characters, which can break the record and prevent proper verification."\"v=spf1 include:cust-spf.exacttarget.com include:spf.mtasv.net ~all\""
 Gmail can't confirm the email's integrity. The absence of a DMARC policy, or having one set to p=none without proper alignment, also signals to mailbox providers that you're not fully authenticating your emails. This could also be why Gmail might flag an email as suspicious due to low sender reputation.
Gmail can't confirm the email's integrity. The absence of a DMARC policy, or having one set to p=none without proper alignment, also signals to mailbox providers that you're not fully authenticating your emails. This could also be why Gmail might flag an email as suspicious due to low sender reputation. Gmail. Another often overlooked aspect is your IP address or domain ending up on a email blocklist (or blacklist), which significantly degrades your sender reputation. Even if your authentication is technically correct, a poor reputation can override it, leading to messages being blocked or spam filtered.
Gmail. Another often overlooked aspect is your IP address or domain ending up on a email blocklist (or blacklist), which significantly degrades your sender reputation. Even if your authentication is technically correct, a poor reputation can override it, leading to messages being blocked or spam filtered. Gmail accounts, ensure you're not forwarding emails in a way that breaks authentication, which can lead to alerts like Gmail marking emails as phishing. If you're using a custom domain with
Gmail accounts, ensure you're not forwarding emails in a way that breaks authentication, which can lead to alerts like Gmail marking emails as phishing. If you're using a custom domain with  Gmail, ensure your DNS records are correctly configured for your Google Workspace setup. These steps are fundamental to preventing your emails from being flagged.
Gmail, ensure your DNS records are correctly configured for your Google Workspace setup. These steps are fundamental to preventing your emails from being flagged. Gmail displays 'unverified sender' or 'cannot verify' warnings.
Gmail displays 'unverified sender' or 'cannot verify' warnings. Gmail verifies the sender, often showing a checkmark or trusted status.
Gmail verifies the sender, often showing a checkmark or trusted status. Gmail marking your emails as spam. Mailbox providers track various signals, including complaint rates, bounce rates, spam trap hits, and user engagement (opens, clicks, replies). Consistently sending unwanted emails, even if authenticated, will damage your domain's standing.
Gmail marking your emails as spam. Mailbox providers track various signals, including complaint rates, bounce rates, spam trap hits, and user engagement (opens, clicks, replies). Consistently sending unwanted emails, even if authenticated, will damage your domain's standing. Gmail might flag your emails as unverified or spam is crucial for effective email communication. It's almost always related to a fundamental issue with your email authentication, or your sender reputation, or both. Taking immediate action to audit and correct your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records is the most effective first step.
Gmail might flag your emails as unverified or spam is crucial for effective email communication. It's almost always related to a fundamental issue with your email authentication, or your sender reputation, or both. Taking immediate action to audit and correct your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records is the most effective first step.