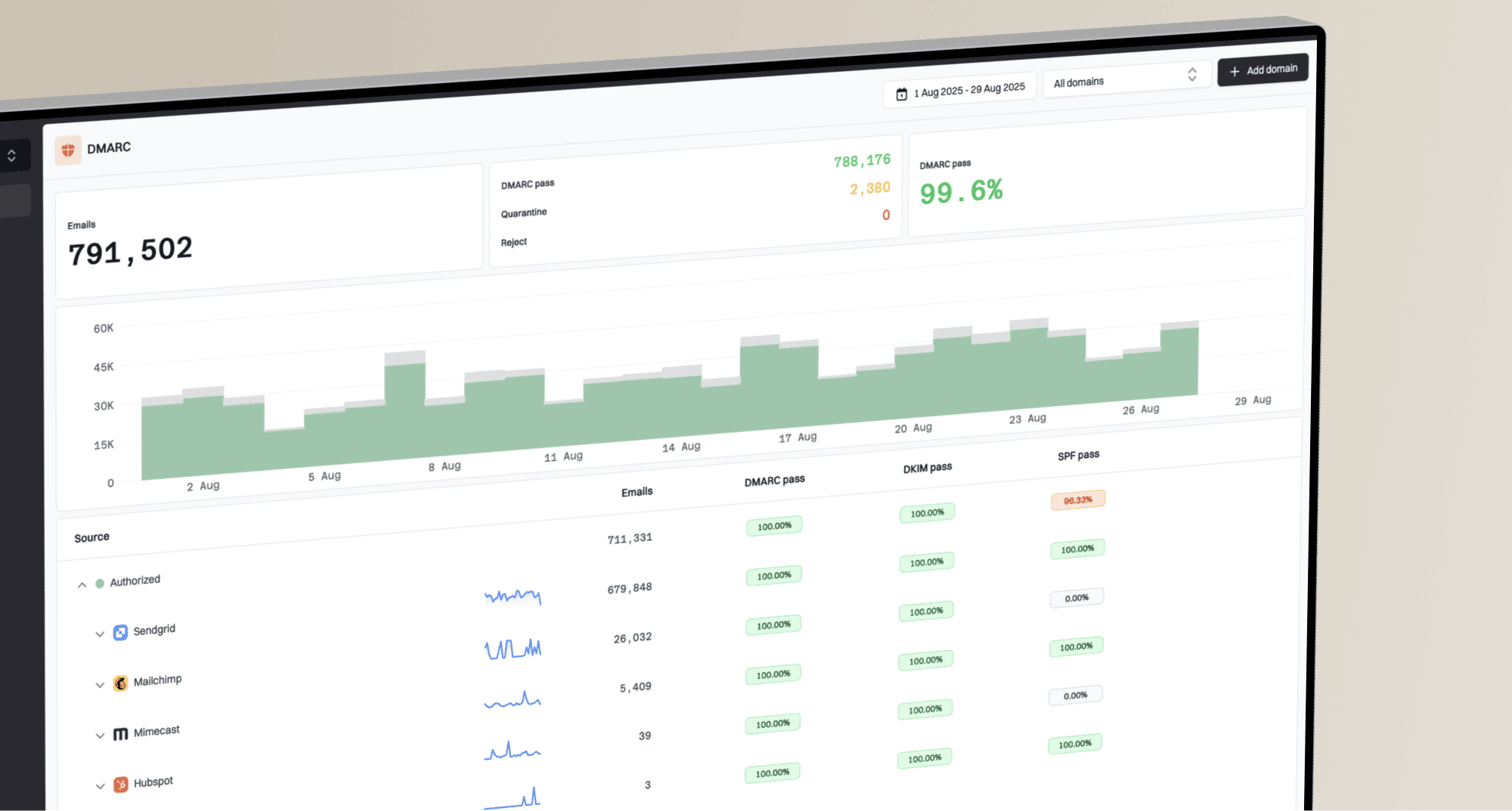
How do I implement Gmail Annotations and troubleshoot common issues?

Michael Ko
Co-founder & CEO, Suped
Published 7 May 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
6 min read

 Gmail, providing the structured data it needs to display rich previews. The @context field should point to http://schema.org/, while the @type specifies the type of offer, such as DiscountOffer or SaleEvent.
Gmail, providing the structured data it needs to display rich previews. The @context field should point to http://schema.org/, while the @type specifies the type of offer, such as DiscountOffer or SaleEvent. Google's guidelines to display correctly.
Google's guidelines to display correctly.<html> <head> <script type="application/ld+json"> [{ "@context": "http://schema.org/", "@type": "DiscountOffer", "description": "Save 20% on your first order", "discountCode": "SAVE20", "availabilityStarts": "2024-05-19T00:00:00-07:00", "availabilityEnds": "2025-09-09T23:59:59-07:00", "image": "https://example.com/images/promo_banner.jpg", "logo": "https://example.com/images/company_logo.png" }] </script> </head> <body> <!-- Your email content goes here --> </body> </html>