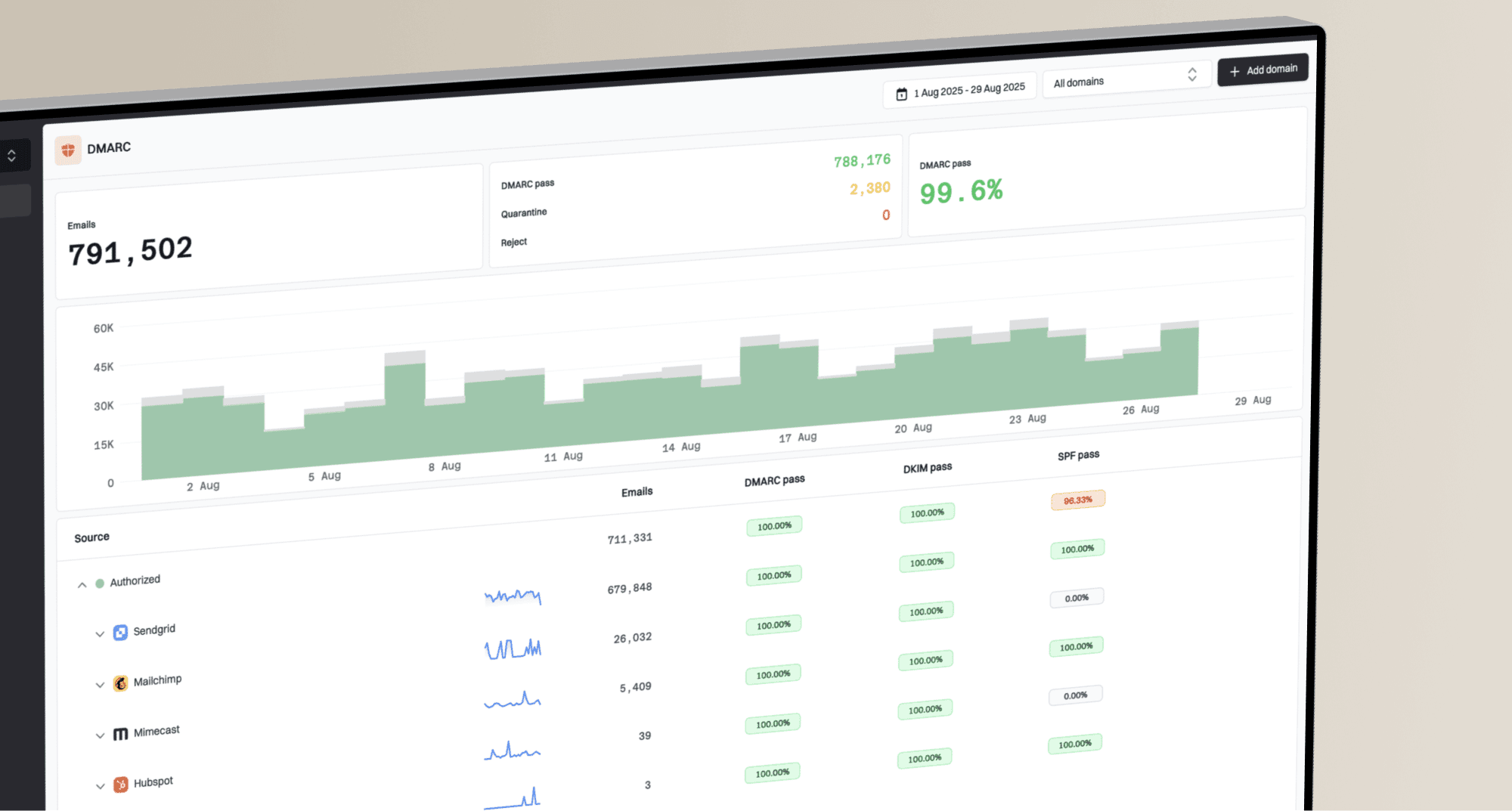
How do I identify who reported my emails as spam in Gmail and how to reduce complaints?

Matthew Whittaker
Co-founder & CTO, Suped
Published 26 Jun 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
6 min read

<a href="https://yourdomain.com/unsubscribe" style="color: #007bff; text-decoration: underline;">Unsubscribe from this list</a> List-Unsubscribe: <mailto:unsubscribe@yourdomain.com?subject=unsubscribe>, <https://yourdomain.com/unsubscribe>
|
|
|---|---|
Active (opens, clicks) | Continue sending engaging content. |
Inactive (no engagement in 30-60 days) | Initiate a re-engagement campaign. |
Unresponsive (no engagement after re-engagement) | Suppress or remove from mailing list to protect reputation. |
Spam Complainer | Immediately remove from all lists to avoid further complaints and potential blacklisting (or blocklisting). |