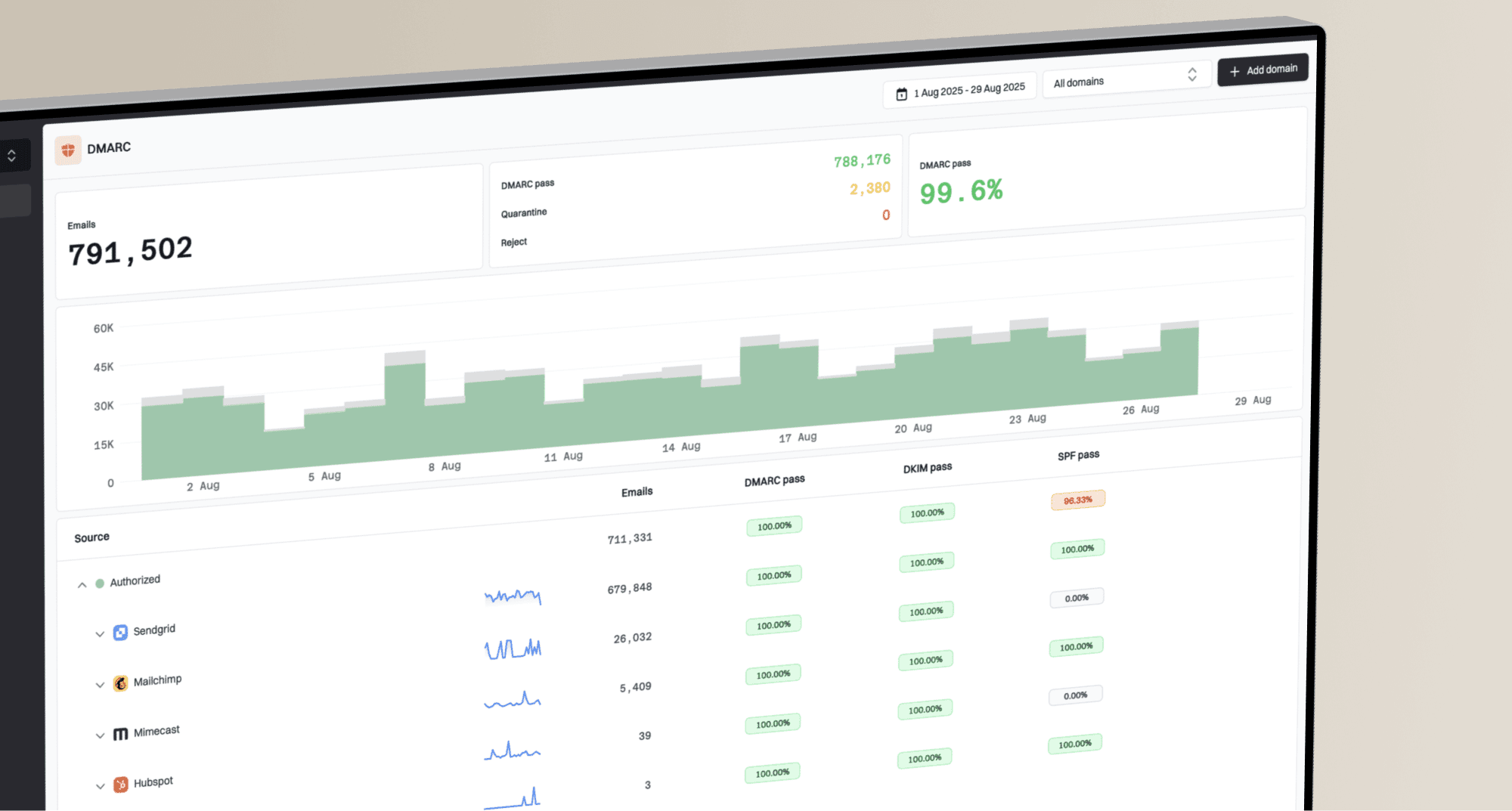
Can sending to a bad email list affect the open rates of a previously sent good list?

Michael Ko
Co-founder & CEO, Suped
Published 30 Jun 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
7 min read

 Gmail and
Gmail and  Outlook constantly monitor your sending practices to assess your trustworthiness. A sudden drop in engagement or a spike in complaints from a bad email list can send negative signals that ripple across all your campaigns, including those already delivered.
Outlook constantly monitor your sending practices to assess your trustworthiness. A sudden drop in engagement or a spike in complaints from a bad email list can send negative signals that ripple across all your campaigns, including those already delivered. Microsoft (Outlook/Hotmail) and
Microsoft (Outlook/Hotmail) and  Google (Gmail), are known to re-evaluate already delivered mail and move it out of the inbox if subsequent negative signals are detected.
Google (Gmail), are known to re-evaluate already delivered mail and move it out of the inbox if subsequent negative signals are detected.