What is the role of the 'cv' tag in an ARC-Seal header?

Michael Ko
Co-founder & CEO, Suped
Published 5 Jan 2025
Updated 5 Oct 2025
5 min read
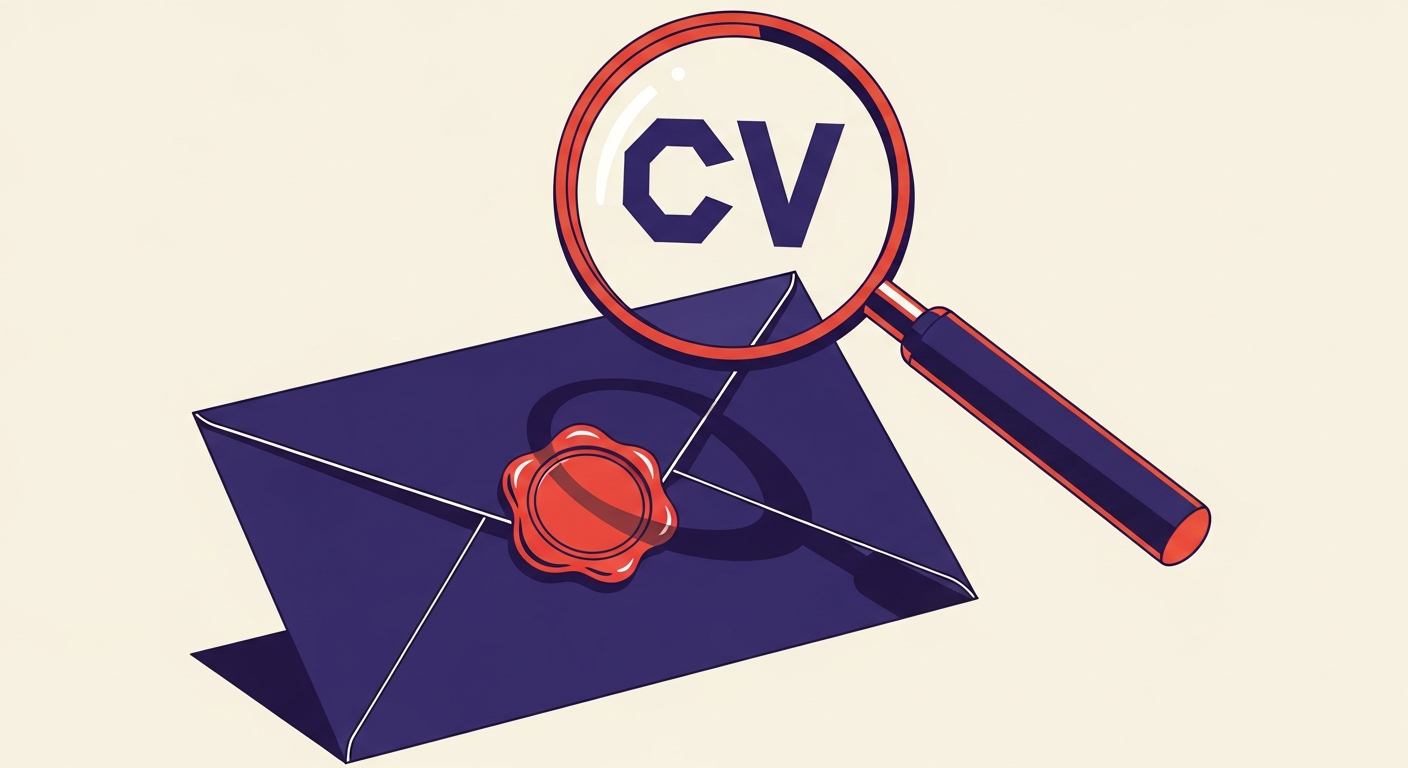


ARC-Seal: i=1; a=rsa-sha256; cv=none; s=arc; t=1678886400; d=example.com; bh=xyz; h=from:to:subject; b=ABCDEFG
 Google and
Google and  Microsoft rely heavily on authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to filter spam and protect users. However, legitimate forwarding services can inadvertently break these authentications. ARC, through its 'cv' tag, provides a mechanism to confirm the original authentication status, helping these messages reach the inbox.
Microsoft rely heavily on authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to filter spam and protect users. However, legitimate forwarding services can inadvertently break these authentications. ARC, through its 'cv' tag, provides a mechanism to confirm the original authentication status, helping these messages reach the inbox.