What SPF mechanism includes the IP addresses of the sending domain?

Michael Ko
Co-founder & CEO, Suped
Published 16 Feb 2025
Updated 3 Oct 2025
7 min read
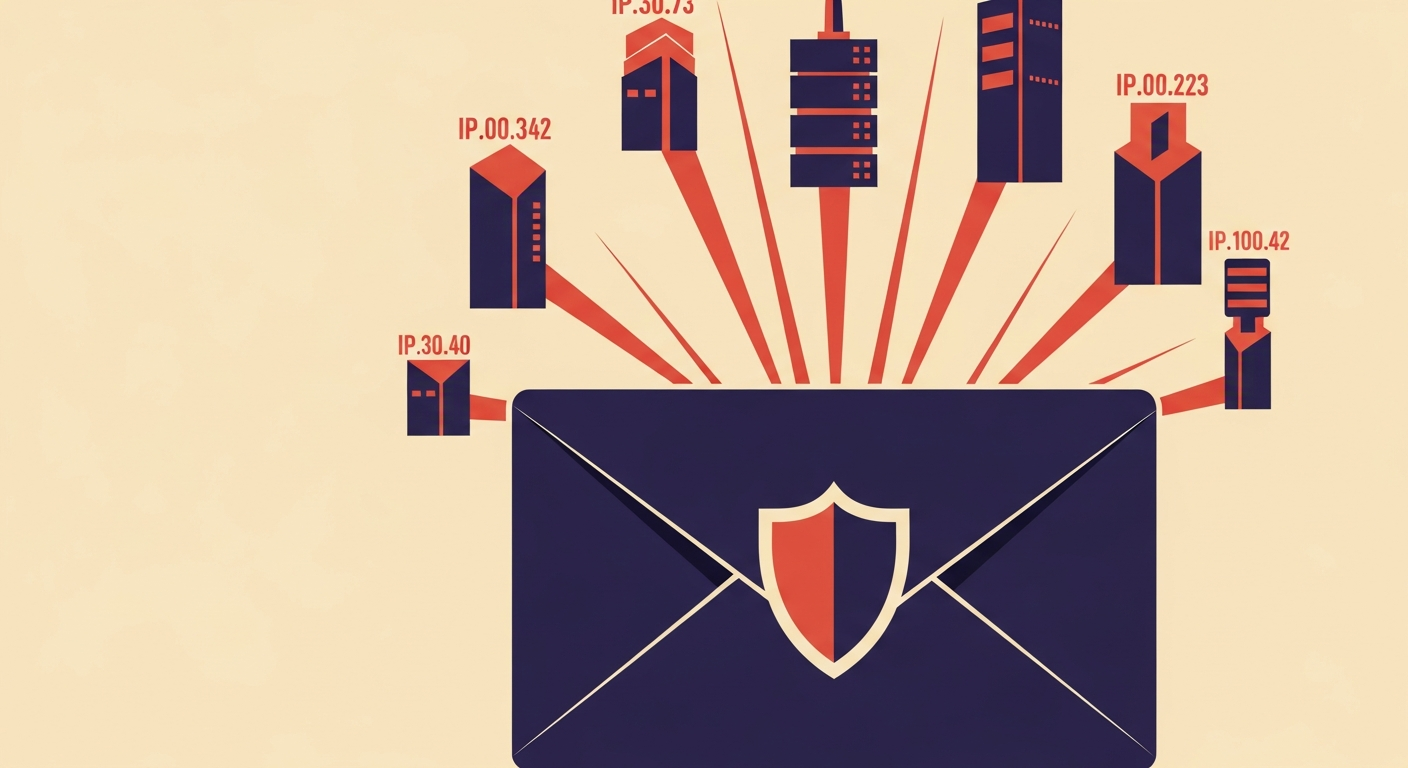


v=spf1 ip4:192.0.2.1 ip4:198.51.100.0/24 -all
 setting up SPF provides further details.
setting up SPF provides further details. SPF 10-DNS-lookup limit. Exceeding this limit can lead to SPF validation failures. Services like Suped's SPF Flattening can help manage this complexity.
SPF 10-DNS-lookup limit. Exceeding this limit can lead to SPF validation failures. Services like Suped's SPF Flattening can help manage this complexity.