Does a DMARC 'rua' URI require 'mailto:' prefix?

Matthew Whittaker
Co-founder & CTO, Suped
Published 9 May 2025
Updated 30 Oct 2025
6 min read


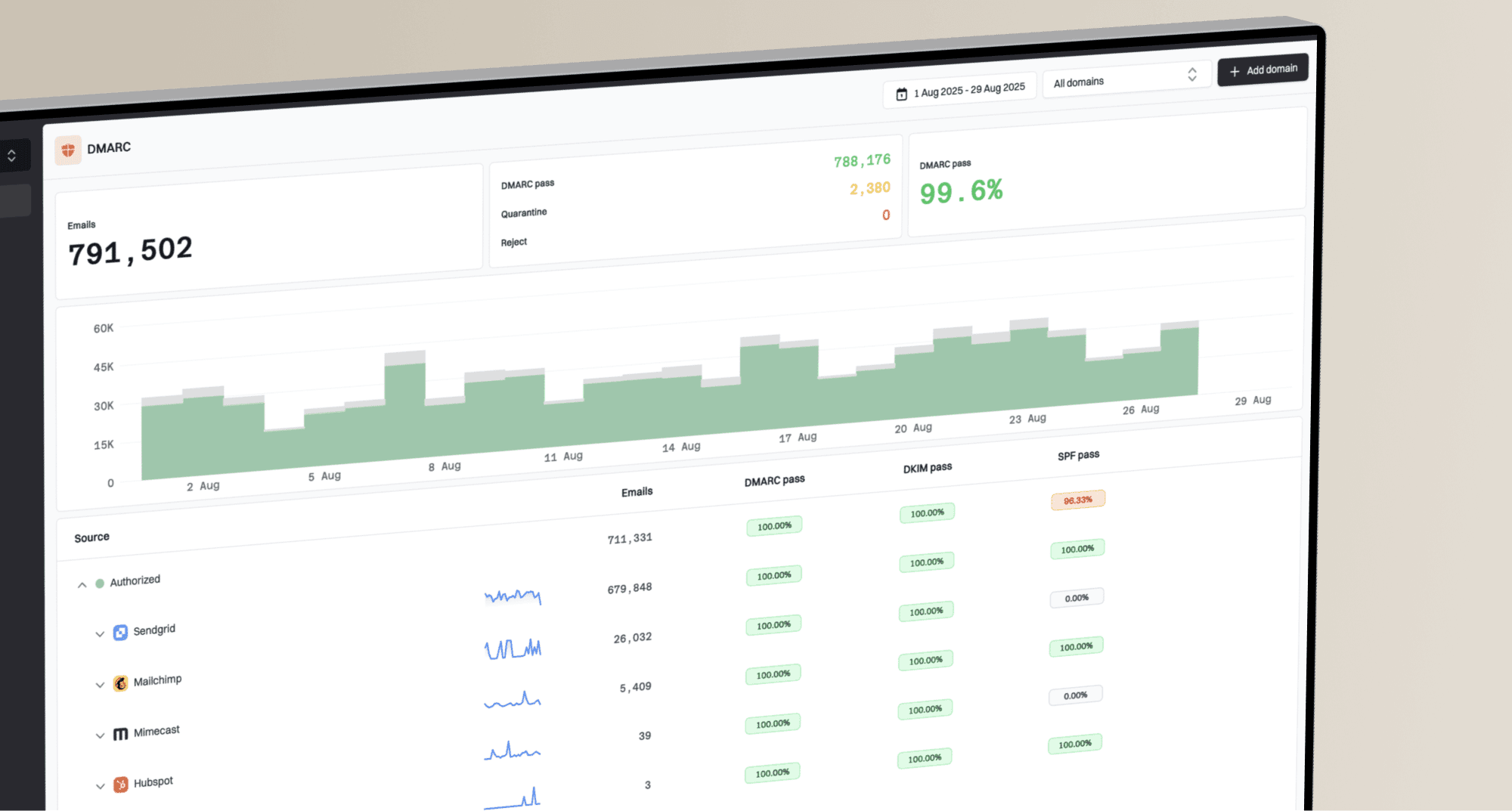
 Google, Yahoo, Outlook) and analyze them using a DMARC monitoring platform. Without these reports, it is difficult to accurately assess your email security posture and make informed decisions about your DMARC policy.
Google, Yahoo, Outlook) and analyze them using a DMARC monitoring platform. Without these reports, it is difficult to accurately assess your email security posture and make informed decisions about your DMARC policy.v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@yourdomain.com; fo=1;
 Suped simplify the process of configuring your DMARC records and analyzing the incoming reports, offering actionable recommendations to improve your email security.
Suped simplify the process of configuring your DMARC records and analyzing the incoming reports, offering actionable recommendations to improve your email security.
|
|
|---|---|
Includes the mailto: prefix. | Omits the mailto: prefix. |
Example: rua=mailto:reports@example.com | Example: rua=reports@example.com |
Reports will be delivered correctly. | Reports will not be delivered, leading to monitoring failures. |

 Suped provides real-time alerts for these critical DMARC issues, ensuring you are immediately aware of any problems.
Suped provides real-time alerts for these critical DMARC issues, ensuring you are immediately aware of any problems. Suped for DMARC monitoring simplifies compliance. We provide AI-powered recommendations to fix configuration issues, including correct URI formatting. Our unified platform combines DMARC, SPF, and DKIM monitoring, offering a comprehensive view of your email security and deliverability. With Suped, you get not just data, but actionable insights.
Suped for DMARC monitoring simplifies compliance. We provide AI-powered recommendations to fix configuration issues, including correct URI formatting. Our unified platform combines DMARC, SPF, and DKIM monitoring, offering a comprehensive view of your email security and deliverability. With Suped, you get not just data, but actionable insights. Suped, you can ensure your DMARC implementation is effective, providing clear visibility into your email sending practices and protecting your brand from spoofing and phishing attacks.
Suped, you can ensure your DMARC implementation is effective, providing clear visibility into your email sending practices and protecting your brand from spoofing and phishing attacks.