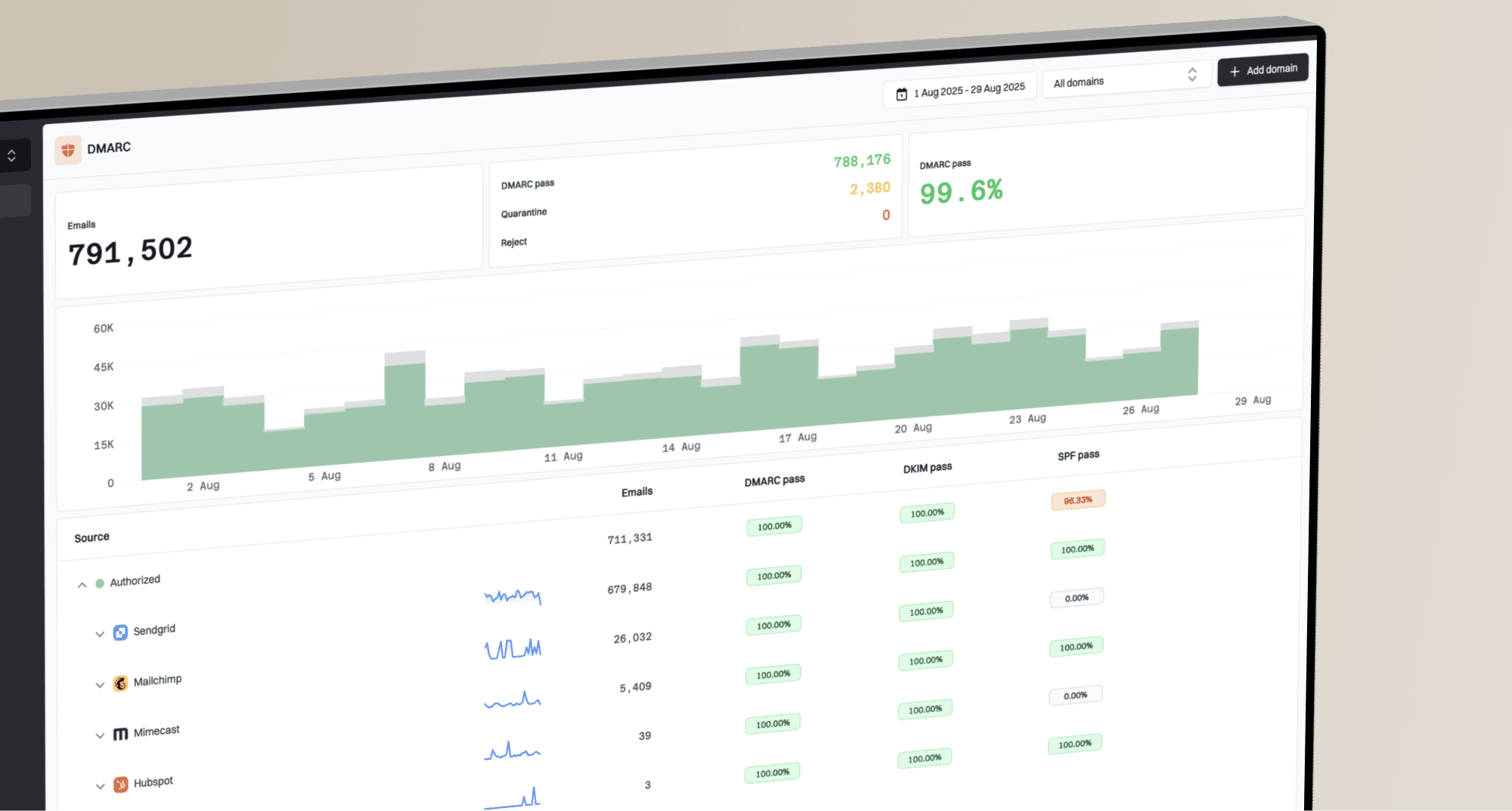
What is the recommended DKIM key algorithm?

Matthew Whittaker
Co-founder & CTO, Suped
Published 12 Jun 2025
Updated 18 Sep 2025
6 min read


selector1._domainkey IN TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDz9N...; a=rsa-sha256; s=email; t=s;"
 Microsoft, are deprecating or penalizing these keys.
Microsoft, are deprecating or penalizing these keys.