What is the 'arc-status' field in the ARC-Authentication-Results header?

Michael Ko
Co-founder & CEO, Suped
Published 26 Jul 2025
Updated 12 Oct 2025
5 min read

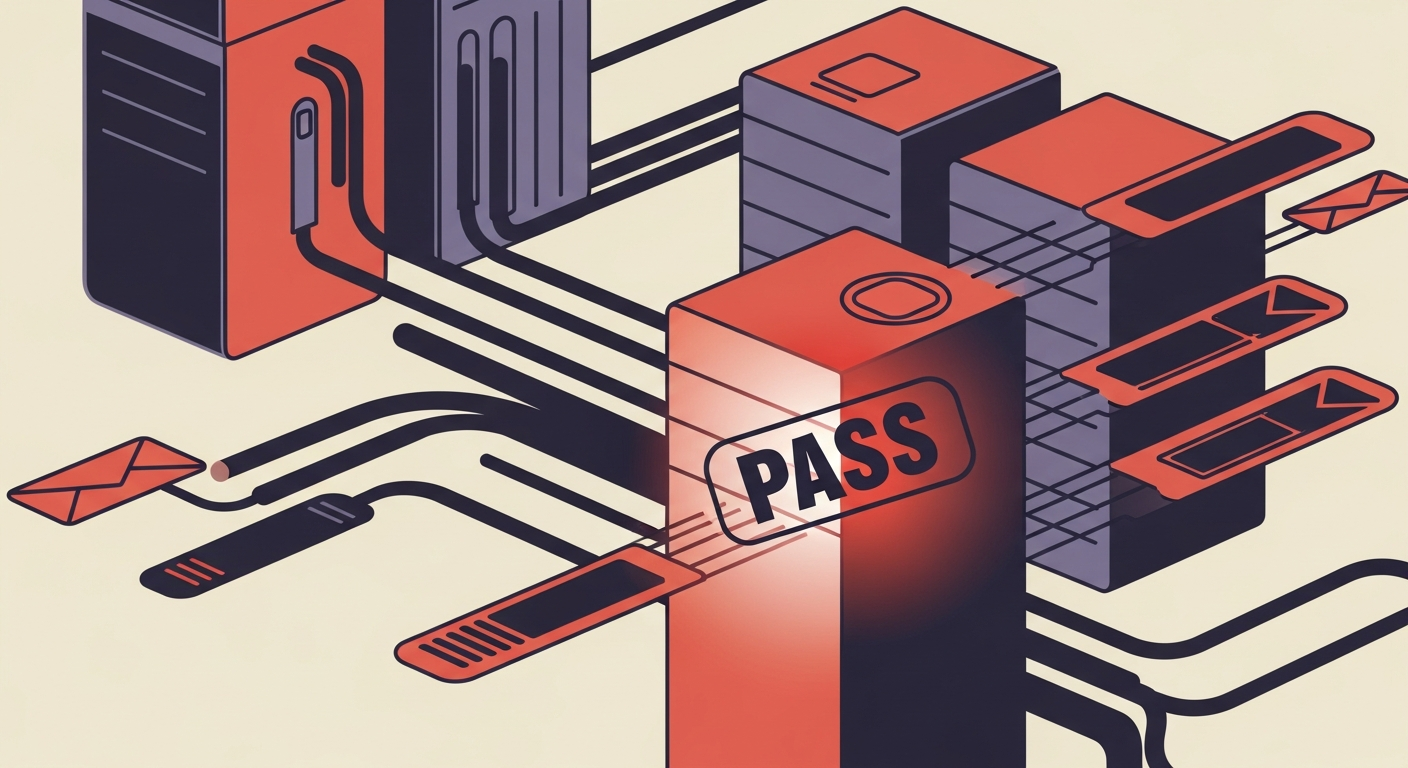
ARC-Authentication-Results: i=1; mx.google.com; arc-status=pass dmarc=pass (p=none sp=none dis=none) smtp.from=example.com

|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Forwarded email | SPF/DKIM often break, leading to DMARC failure. | Original authentication preserved, aiding DMARC validation. |
Deliverability | High risk of emails being sent to spam or rejected. | Increased likelihood of inbox delivery for legitimate mail. |
Sender reputation | Can be negatively impacted by DMARC failures. | Protected by providing context for authentication issues. |
 Suped offer comprehensive DMARC monitoring that includes insights into ARC. Our AI-powered recommendations tell you exactly what actions to take to fix authentication issues, while real-time alerts ensure you're immediately notified of potential problems. With a unified platform for DMARC, SPF, and DKIM, you get a complete picture of your email authentication, helping you maintain optimal deliverability and protect against spoofing and phishing attacks.
Suped offer comprehensive DMARC monitoring that includes insights into ARC. Our AI-powered recommendations tell you exactly what actions to take to fix authentication issues, while real-time alerts ensure you're immediately notified of potential problems. With a unified platform for DMARC, SPF, and DKIM, you get a complete picture of your email authentication, helping you maintain optimal deliverability and protect against spoofing and phishing attacks. Suped, you gain powerful tools like SPF flattening and real-time alerts to manage these complexities, ensuring your emails consistently reach the inbox.
Suped, you gain powerful tools like SPF flattening and real-time alerts to manage these complexities, ensuring your emails consistently reach the inbox.